
Testicular prosthesis is usually a silicone implant of oval shape, filled with sillicone gel or saline, that can be placed in scrotum for cosmetic effect. In pediatric population these are adolescents after testicular torsion, after congenital testicular dysgenesia or agenesia, after neoplasms of the testis or treated for sexual differentiation disorders.
Implants are manufactured by a few companies. They come in 3 or five different sizes, from 20 to 50mm. Age of surgery is a subject of some controversy. In my opinion age of 15 or 16 is most appropriate, because th testis reaches it’s final size. Rarely we can do it earilier to promote sexual identification and psychosexual development in patient with sexual differentiation disorders. Unfortunetely until 8-10 yo the testes have ‘children” size which hardly changes and is between 15-20mm. So the products on the market are simply too big. To make things worse, children that would benefit from early implant often have small, flat scrotum, that can not accomodate the prosthesis.
Surgery
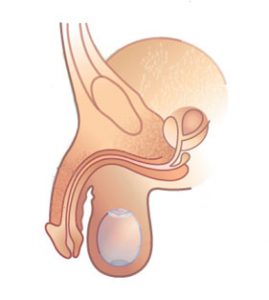
Can be performed on the outpatient basis. There are even places, where it is performed local anesthesia, though I can hardly imagine this. Optimal is shallow general anesthesia with local bupivacaine, as usually in surgery of this region. One dose prophylactic antybiotic is recommended. Surgery usually lasts about 20 minutes. Incision is made high over the pubic bone on the level of penis or even slightly higher. From here we reach down the scrotum and create adequate space inside it, caring for hemostasis. The pole of the implant should be fixed to subcutaneous tissue in the lowest part of the scrotum. The upper part of the scrotum should be closed with sutures, to hold the prosthesis in proper position. Skin wound can be closed with intracutaneous running absorbable suture.
The whole hospital stay is 4 to 5 hours. On the way home the patient should have some company. After anesthesia he should not drive. Pain relief medications are needed usually for 2 days. For 3 days normal activity should be limited, and exercise avoided for 2-3 weeks. Wound dressing can be removed on 5th postoperative day. It is closed with running absorbable intracutaneous suture, so there are no stiches to be removed. Some oedema and hardening of scrotal and inguinal region are normal and disappear in weeks.
Choice of implant

The implant should be choosen together with the patient during preoperative visit. With ultrasound we measure present testis and choose from brands available. Patients have their own preferences sometimes. It is better to choose slightly smaller prosthesis if exact match is not possible. Currently on Polish market we can find implants from 3 different manufacturers. They all have plain surface and are naturally soft. On one pole they have an openning for suture fixing to subcutanous tissue. All these implants cost about 250EUR. Only a few years ago there was an official dealer on Polish market that sold prostheses for almost half the price. They were heavy and unnatularrly firm, but mainly public hospitals bought them, caring only about the price. These implants should be forbidden and dealers investigated. On the web one can find many complaints of unhappy patients carrying these stone-like implants.
Complications
It is common knowledge, that implantation of foreign body may cause local inflammation and suppuration, especially when it is surrounded by heamatoma. Thats why during surgical procedure careful hemostasis and antibacterial prophylaxis are important. Usually if the prosthesis is surrounded by pus it must be removed. From my experience I heard about this situation only if someone implanted the prosthesis through the scrotum.
If the implant is poorely fixed in small scrotum it can move upwards into inguinal canal. I’ve encountered this complication myself when implanting both side simultaneously in small scrotum.
I’ve written above about stone -hard pseudo-prostheses. The enforced pole on the implent with fixing suture can sometimes be palpated and does not feel natural. It bothers some patients and I don’t know why manufaturers do nothing about it. I’ve read somewhere that with time the fibrous capsule may form around the implant (the phenomenon know from breast implants). Direct trauma to the prosthesis may result with it’s rupture and requires it’s removal.